How to delete a user in custom Artisan Command line in Laravel?
Laravel is a full-stack framework that offers a lot of artisan commands to automate various actions, like creating a controller, seeding the database, and starting the server. However, when you build custom solutions, you have your own special needs, which could include a new command. Laravel doesn’t limit you to only its commands; you can create your own in a few steps.
Here are the steps for how to create a new artisan command.
Step 1: Create a new Laravel application
|
1 |
Laravel new custom |
Step 2: Create a command
Use the make:command command to create a new command. Simply pass in the command name, like so:
|
1 |
php artisan make:command RemoveUser |
The command creates a file named RemoveUser.php, named after the command name, in a newly created Commands directory in the Console folder.
The generated file contains the configurations of the newly created command that are easy to understand and edit.
Step 3: Customize command
First, set the command signature. This is what would be put after php artisan to run the command. In this example, we will use remove:user, so the command will be accessible by running:
|
1 |
php artisan make:command RemoveUser |
To do this, update the $signature property of the command, like this:
|
1 |
Protected $signature = ‘remove:user’ {id}; |
Next, set up a suitable description that would show up when php artisan list displays the command with other commands.
To do this, update the $description property to match this:
|
1 |
Protected $description = ‘Remove user all Data’; |
Finally, in the handle() method, perform whatever action you intend it to perform. In this example, the number of users on the platform is echoed.
12345678
public function handle(){ $userId = $this->argument('id'); $delete[]=explode($usereId); foreach($delete as $id){ DB::table('users')->whereIn(id, $id)->delete(); $this->info('Delete users successfully!'); }
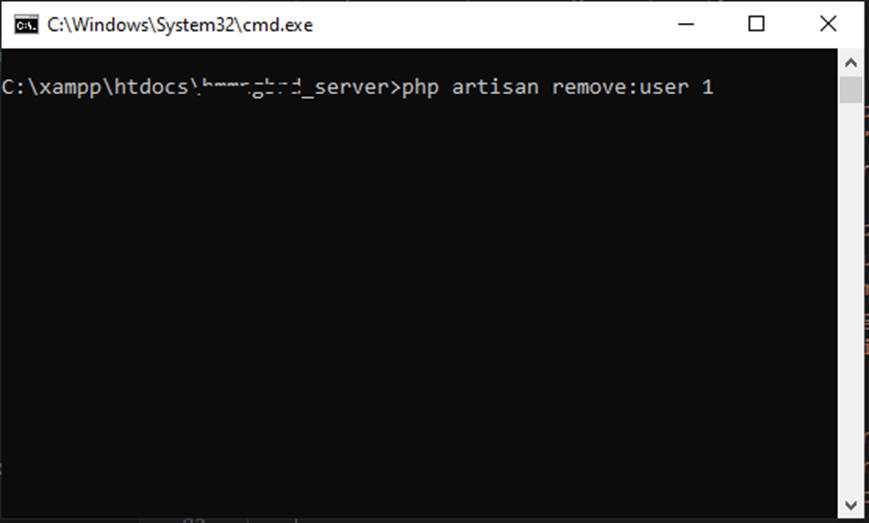
Step 4: Test command
In the terminal, run the command to see the number of users in your database.
|
1 |
php artisan remove:user |
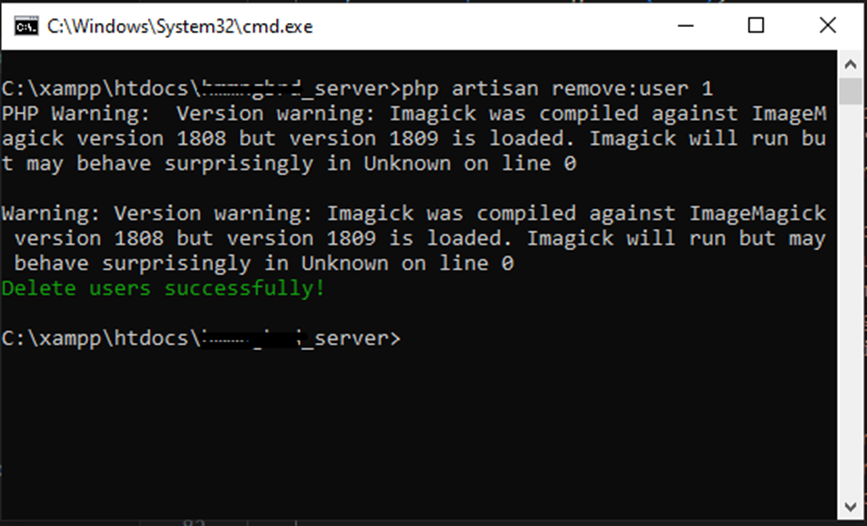
Now, when php artisan remove:user 1 is run, you should see something like this: